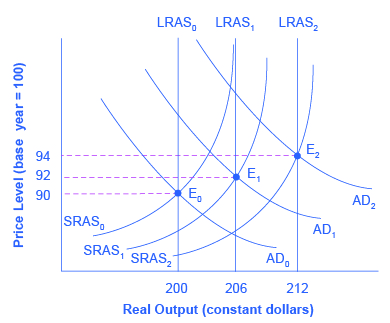
Fiscal policy involves the monetary authorities’ decisions regarding the level of inflation and/or short term interest rate (which affects long-term rates) to support sustainable levels of aggregate demand.
Contractionary fiscal policy consists of a combination of two elements. The first element is a decrease in government spending. This reduces the quantity of money in circulation, reducing both the supply of liquidity and its velocity. In addition, it will also lead to a reduction in the prices paid for goods. This will reduce the purchasing power of consumers’ incomes.
The second part of contractionary fiscal policy is an increase in the tax burden. Tax increases are typically achieved by either increasing individual income or corporate taxation. Both effects tend to increase the cost of production.
What Is an Example of a Contractionary Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy can be defined as the government’s spending and taxing decisions. This affects the overall economic growth, inflation, unemployment rate, interest rates, and the budget deficit. The goal of the central bank is to maintain low inflation while keeping the economy stable. A contractionary fiscal policy is one that reduces the amount of money in circulation.
A contractionary fiscal policy can also reduce consumer demand by limiting the availability of credit. If consumers are forced to save more, they will spend less, and this could cause the economy to slow down.
In addition, a contractionary fiscal policy would increase the federal debt. In other words, it would make the government have to borrow more money to pay for its bills.
So, a contractionary fiscal policy is one that limits the supply of currency. It decreases the total amount of cash in the economy, and this can affect the way people behave.
For example, if the Federal Reserve cuts the number of dollars in circulation, then this will likely lower prices.
What Is Contractionary and Expansionary Fiscal Policy?
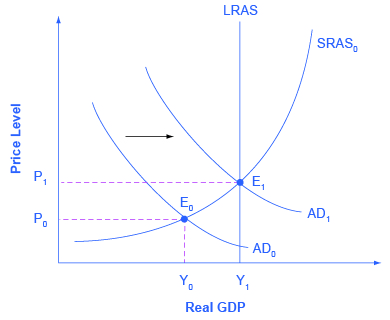
Fiscal policies refer to the actions taken by governments in order to stimulate the economy. When a government takes steps to increase spending, this is referred to as an expansionary fiscal policy.
However, when the government cuts back on its spending, this is known as a contractionary fiscal policy.
This article explains the difference between these two terms.
A contractionary fiscal policy reduces public spending, while an expansionary one increases it. However, the key thing to remember here is that both of them affect the overall size of the budget deficit.
When the government spends more money than it receives in revenue, the budget surplus will be reduced.
If the opposite happens, then there will be a reduction in the budget deficit.
Therefore, a contractionary fiscal policy can lead to an economic downturn.
On the other hand, an expansionary fiscal policy leads to an improvement in the economy.
As you can see, the type of fiscal policy that you choose will depend on whether you want to reduce or increase the level of unemployment.
What Is the Difference Between Contractionary and Expansionary Policy?
Fiscal policy refers to the government’s decision regarding how much money it spends. When the government decides to spend more than they take in through taxes, this is known as an “expansionary” fiscal policy. On the other hand, when the government takes in more money than it spends, it is said that the fiscal policy is “contractionary.”
When the government runs a deficit, the result will be inflation. This means that prices for goods and services rise due to increased demand. Inflation is a monetary phenomenon. It occurs when the central bank increases the supply of currency in circulation. The increase in the number of dollars causes higher prices for consumer goods.
As a result, the federal government must raise taxes to compensate for the loss of tax revenue. However, this is not always possible. As a result, the government may choose to cut spending instead.
This is why the United States has experienced three major recessions since World War II. Each time, the government chose to reduce its budget deficits by cutting back on spending.
How Does Contractionary Monetary Policy Reduce Inflation?
Fiscal stimulus is a type of fiscal policy that involves increasing government spending in order to stimulate the economy. When the federal government spends more money than it takes in, this leads to an increase in the size of the national debt. As the amount of the nation’s debts increases, so does the total value of all the bonds issued by the US Treasury.
When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, they do two things. First, they make it harder for individuals and businesses to borrow funds from the central bank. Second, they prevent banks and other financial institutions from lending out their reserves to borrowers. This means that the supply of reserve balances falls, while the demand for them rises.
As a result, the Fed’s balance sheet becomes larger, thereby reducing the quantity of cash available in the system. If the Fed continues raising its rate, the effect is that the economy shrinks, leading to lower prices and wages. The net effect of this is that the Fed is trying to get inflation back under control.
What Is the Goal of Contractionary Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy refers to the decisions made by government officials regarding how much money should be spent on public goods such as health care, education, infrastructure, etc. The main objective of any government is to spend its budget in order to achieve certain goals.
When a country’s economy is growing rapidly, governments tend to increase spending so that they can provide more services. This helps to create jobs and boost economic activity. However, when an economy begins to contract, it becomes harder for politicians to keep up with the costs of providing essential services. As a result, many countries have implemented policies that encourage them to cut back on their spending.
These policies are known as “contractionary” because they cause a reduction in the amount of money being spent. In other words, these measures reduce the size of the pie.
What Is the Goal of Contractionary Fiscal Policy?
The goal of contractionary fiscal policy is to help stabilize an economy. When a recession occurs, businesses start laying off workers, which causes unemployment rates to rise.
Does Contractionary Policy Increase Inflation?
There is a lot of debate surrounding whether fiscal stimulus increases inflation. This article looks at how this question can be answered using data from the Great Recession.
Inflation refers to an upward trend in the prices of goods. When the government spends more money than it takes in, the result is that the budget deficit rises. As the budget deficit grows larger, the government needs to borrow more and more money.
If a country does not have enough foreign currency to pay its debts, then the central bank will need to print new dollars or euros. Printing money causes inflation because the supply of cash is increased. The higher demand for cash drives up prices.
When the economy is in recession, the opposite happens. A contracting economy means that the private sector must cut back on spending. Because it cannot afford to buy all the products and services that it wants, the amount of money circulating in the economy falls.
As the amount of money shrinks, the central bank has to reduce the number of dollars or euros in circulation.
What Are the Effects of Contractionary Fiscal Policy?
Fiscal policy is one of the most important tools that a government can use to manage its economy. This includes things like taxes, spending, and interest rates.
When governments have a deficit, they increase their borrowing. When this happens, people who own bonds will sell them in order to receive more money. As these bondholders buy other assets, the price of stocks and commodities rises. The opposite occurs when there is an excess of funds.
In addition to raising prices, a higher budget deficit can also cause inflation. Inflation is simply when the cost of goods and services rise. If a country has high levels of inflation, it means that consumers are paying more for the same products.
If a government is running a surplus, then there is less demand for debt. This causes the value of the currency to fall.
The result of all of this is that the government can change the overall level of economic activity. Contractionary fiscal policies include things such as tax cuts, increased spending on public works projects, and reduced interest rates.
What Is an Example of Expansionary Fiscal Policy?
Expansionary fiscal policies are used by central banks to stimulate economic activity. The Federal Reserve uses this type of monetary policy in order to increase the money supply, which increases the total amount of cash in circulation. This leads to higher inflation rates.
However, contractionary fiscal policies are used by governments to reduce spending. The government cuts taxes and reduces the overall level of public expenditure.
Inflation can be defined as a rise in prices that causes real wages to fall. When the economy is growing rapidly, it’s possible for inflation to occur. However, when the economy slows down, deflation becomes more likely. Deflation is when prices drop, and real wages start to rise.
When a country experiences high levels of inflation, it means that its currency is losing value. If you want to protect your savings from falling currencies, then you should consider investing in foreign exchange. You will find that this investment option offers you better returns than any other form of saving.
What Is the Difference Between Expansionary and Contractionary Fiscal Policy Quizlet?
Expansionary fiscal policy refers to a situation where government spending increases, while taxes decrease. This type of policy tends to be used by governments that want their economies to grow faster.
On the other hand, contractionary fiscal policy refers to a situation where government spending decreases, while taxes increase. This type of policy tends to be used by governments that don’t want their economies to grow too quickly.
In order to understand the differences between these two policies, you need to first know what they mean. When the government spends more money than it takes in, it is said to have an “expansionary” budget deficit. On the other hand, when the government spends less money than it takes in, it is said to have a “contractionary” budget deficit.
As you can imagine, there are pros and cons associated with each one of these situations. If the economy is growing rapidly, then an expansionary budget deficit may help to stimulate growth. However, if the economy starts to slow down, then a contractionary budget deficit could cause problems.
Contractionary Fiscal Policy Tagalog
Fiscal policy is the set of policies that governments use to manage their budgets. This includes things like government spending, taxation, borrowing, and debt.
When a country experiences an economic downturn, it can sometimes be difficult for them to balance their budget. When this happens, the government will usually reduce its expenditure.
This means that the economy will shrink, and the unemployment rate may rise.
However, there are times when it’s necessary to increase the amount of money that the government spends on things such as education and healthcare.
There are also times when the government needs to borrow more money.
In these cases, the government will have to raise taxes. If they don’t do this, then they could end up with a deficit.
If a country has a large public sector, it may find that it has trouble balancing its budget. In this case, the government should cut back on the number of civil servants that it employs.
Contractionary Fiscal Policy Is Intended to Combat Recessions
Fiscal policy refers to the way that governments spend their money. If you want to know more about how this affects the economy, then you should read the article below. This guide explains why fiscal policy can be used to stimulate the economy.
In the United States, there are two main types of fiscal policy. The first type involves increasing government spending. This will usually result in increased economic activity. However, it may also lead to inflation and higher interest rates.
The second kind of fiscal policy is known as contractionary fiscal policy. When a country implements this, it reduces its spending and cuts taxes. This leads to lower levels of economic activity.
However, it’s important to note that these policies aren’t always effective. Sometimes, they actually make things worse.
If you have any questions, then you can ask them in the comments section.
point: what is a recession, and when does one occur?