Demand is essential to understanding the behavior of an economy and, consequently, to pricing and marketing decisions. This article provides a comprehensive guide to demand theory, with coverage of both elasticity and determinants of demand. You’ll learn how to analyze market conditions in order to generate demand for your products or services, and you’ll understand the implications of changing demand on pricing, marketing strategies, and business performance.
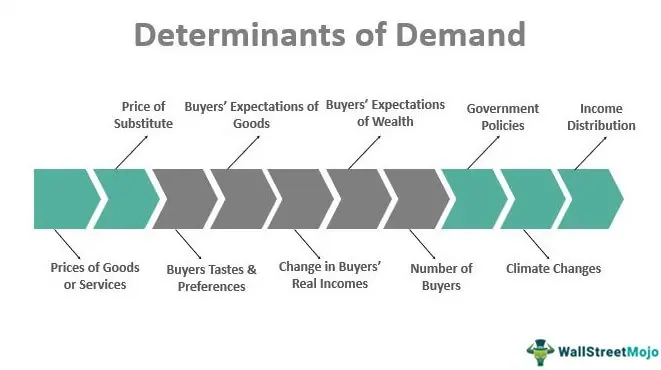
What are the 12 determinants of demand?
Demand is the fundamental cause of economic activity. It is what drives companies to produce goods and services, and it is what causes people to buy those goods and services.
There are 12 determinants of demand: price, income, consumption, investment, savings, debt, export demand, import demand, population size and growth, and political stability.
Each of these factors affects demand in different ways. For example, a rise in income will lead to an increase in consumption and investment. A fall in consumption will lead to a fall in investment and a rise in savings. And so on.
Understanding how each factor affects demand is essential for business owners and economists. It can help them to plan for future growth and ensure that their companies are able to meet customer needs.
What are the 10 factors affecting demand?
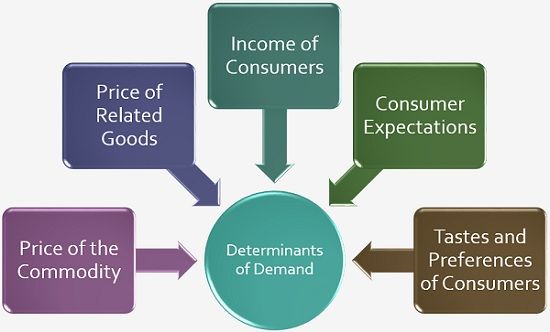
There are many factors that affect demand, and understanding them is essential for businesses. In this article, we will explore 10 key determinants of demand.
1. Price
The price of a product or service is one of the most important factors affecting demand. When the price is too high, consumers may not be able to afford it, and they may choose to purchase another product instead. Conversely, when the price is too low, consumers may be willing to buy more of the product or service than desired.
2. Quality
The quality of a product or service also affects demand. If a consumer believes that the quality of a product is poor, they may choose to purchase an alternative product instead. Conversely, if a consumer believes that the quality of a product is good, they may be more likely to purchase it than an alternative product.
3. Availability
The availability of a product or service also affects demand. If the product or service is not available in sufficient quantities, consumers may not be able to purchase it. Conversely, if the product or service is available in sufficient quantities, consumers may be less likely to purchase an alternate product.
4. Preference
Preferences can vary drastically from person to
What are types of demand?
There are three types of demand- utility, necessity and luxury. Utility demand is the most common type. It refers to the demand for goods and services that satisfy basic needs. Necessity demand refers to the demand for goods and services that are needed for survival. Luxury demand is the demand for goods and services that are not necessary but are desired for their own sake.
What are the 8 factors that affect demand?
Demand is the amount of goods and services that people are willing and able to buy at different prices. It is affected by a variety of factors, including price, availability, and quality.
In this full guide, we will look at the eight factors that affect demand. We’ll explore how each factor affects demand, and we’ll explain what effects each has on the market.
We’ll also provide tips on how to increase demand for your products or services. By understanding how demand works, you can increase your chances of success in the market.
What are the 7 determinants of supply?
There are several factors that influence demand for a good or service. Demand is based on how much someone is willing to pay for a good or service.
Some of the main factors that influence demand for goods and services include price, quality, availability, and satisfaction.
Price is the most important determinant of demand. When the price of a good or service increases, demand decreases. Similarly, when the price of a good or service decreases, demand increases.
Quality is also important because it affects how people perceive a good or service. If the quality of a good or service is poor, people will likely be less satisfied with it and demand for it will decrease.
Availability is also important because it determines how many people can purchase a good or service at one time. If the availability of a good or service is limited, people will likely be less satisfied with it and demand for it will decrease.
Satisfaction is also an important factor because it determines how long someone will continue to purchase a good or service. If someone is unsatisfied with a good or service, they may not purchase it again and demand for it may decrease.
What are the 8 types of demand?
There are 8 types of demand that influence the way products and services are bought and used.
1. DEMAND FOR CONSUMPTION: People need to buy things in order to satisfy their physical needs. This type of demand is usually accompanied by feelings of hunger or thirst, and is driven by emotions such as happiness, anger, or envy.
2. DEMAND FOR TRANSPORTATION: People need to travel to work, school, or other places. This type of demand is driven by practical needs such as money, transportation, or time.
3. DEMAND FOR ENERGY: People use energy to do things such as work, play, or learn. This type of demand is often accompanied by feelings of fatigue or stress.
4. DEMAND FOR THINKING TIME: People need time to think and make decisions. This type of demand is often accompanied by feelings of boredom or anxiety.
5. DEMAND FOR KNOWLEDGE: People need information in order to make decisions or solve problems. This type of demand is often accompanied by feelings of confusion or frustration.
6. DEMAND FOR COMMUNICATION: People interact with others in order to exchange information or ideas
What are the 5 factors of demand?
There are five factors of demand that play a role in determining how much someone will want to buy a product. These factors are price, availability, quality, satisfaction and preference.
Each of these factors has an impact on how much people will want to buy a product. For example, if the price of a product is high, people may not be able to afford it. If the quality of a product is poor, people may not be happy with it. And so on.
In this guide, we’ll explore each of the five factors of demand in detail. We’ll also discuss how each factor affects demand, and how businesses can use this information to their advantage.