Welcome to our full guide on New York State tax rates and collections! In this article, we will outline the major taxes that you may be liable for in New York, how much revenue each tax brings in annually, and how to pay your taxes. We will also provide a full guide on how to collect your taxes from individuals and businesses in New York. So, whether you are a resident or tourist in New York, be sure to read this guide to get an overview of your tax obligations!
Does NYC have a city income tax?
NYC does not have a city income tax. Instead, it levies a personal income tax on residents and non-residents earning an annual income of $200,000 or more. The top marginal rate is 8.82%. There is also a surtax of 2.65% applied to incomes over $500,000. For those who file jointly, the top rate rises to 13.83%. The city also imposes a 3.8% sales tax and an estate tax of up to 25% on estates valued at more than $5 million.
Do I have to pay NYC income tax?
There is no one answer to this question since tax laws can vary from state to state. However, in general, if you are a resident of New York City, you will probably have to pay income taxes on your income.
The main types of income that are taxable in New York City include wages, tips, regular salary, and other forms of earned income. Additionally, certain types of business income and capital gains are usually taxable in New York City too.
Generally speaking, the higher your income, the more tax you will have to pay in NYC. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, people who earn less than $25,000 per year generally don’t have to pay any taxes in NYC. And people who earn less than $5,000 per year generally don’t have to pay any taxes on their Social Security benefits either.
To figure out your tax liability in NYC, you will need to use the IRS’s Tax Calculator tool. This tool will estimate your total tax liability based on your specific income and filing status. You can also get help from a professional tax advisor if you need it.
If you are unsure whether you have to pay taxes in NYC or if you need
Who is subject to New York City income tax?
New Yorkers are subject to income tax in the City of New York. The table below shows the tax rates for individual taxpayers and married couples filing jointly.
Income Tax Rates for New Yorkers Single Filers Married Filers Joint Filers Tax Rate $0-$9,000 10% $9,001-$18,000 12% $18,001-$36,000 13% $36,001-$84,000 15% $84,001+ 20%
The City of New York also imposes a City Income Tax which is imposed on all taxable income above $360,000 for singles and $1 million for married couples filing jointly. The City Income Tax rate is 3%. For more information please visit the NYC Department of Finance website or contact an accountant.
If you are not a resident of New York City but you earn income in the city, you may be subject to non-resident income tax in the city. For more information please contact an accountant.
How much do you pay in taxes in New York City?
New York City residents pay a variety of taxes, including income taxes, city taxes and sales taxes. This guide provides a full breakdown of the different tax rates and how much each costs. Additionally, we provide information on how to pay your taxes in New York City, including instructions on filing taxes online or through the city’s tax collection agency. Finally, we outline the steps you need to take in case of an audit.
Income Taxes in New York City
Residents in New York City who earn income pay federal and state income tax as well as local income tax. The federal income tax rate for individuals is currently 39.6%. The state income tax rate for individuals is 7%–8%, while the city income tax rate ranges from 1.5% to 3.8%. As of 2019, New York City also has a Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) available to those who make less than $50,000 per year. The EITC provides a refundable credit against federal and state income taxes owed, meaning that you can receive a check from the government if you owe taxes and meet certain eligibility requirements.
City Taxes in New York City
City taxes are levied by municipalities all over the United
How do I avoid New York City taxes?
There are a few easy ways to avoid paying city taxes in New York City:
1. Claim your residency outside of New York City. If you don’t live in the city, you’re not obligated to pay city taxes. You can file an annual residency declaration with the New York City Department of Finance or use the online declaration form.
2. Use a tax preparer who specializes in avoiding city taxes. A reputable tax preparer can help you strategize about how to minimize your taxable income and claim any exemptions you may qualify for.
3. Evaluate your situation carefully and consult with a tax attorney if you have any doubts about how to avoid city taxes in New York City. An attorney can help protect your rights and guide you through the complex tax law surrounding residency, exemptions, and deductions in New York City.
Who is exempt from NYC tax?
If you are a resident of New York City, you are exempt from municipal income tax. This means that, regardless of your income, you will only be taxed on the value of your taxable assets in the city (i.e. property, cash, stocks and other investments).
You are also exempt from NY state income taxes if your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is less than $100,000 for individual filers or $200,000 for joint filers. The exemption increases by $25,000 for each additional dependent child you have.
There are some exceptions to the general rule of exemption. For example, if you are a business owner with an office or employee in New York City, you will be taxed on your net income from those activities – not just your assets. And finally, pension and Social Security benefits earned in New York City are taxable regardless of where they are paid out.
If you have any questions about whether you are exempt from NYC tax, consult with an accountant or tax preparer.
Does New York City tax non residents?
Yes, New York City does tax non residents. Non residents are subject to the city’s personal income tax, which is imposed at a rate of 8.84% for individuals and 15.24% for joint returns. The city also imposes an earned income tax of 3.8% on individuals and 7.65% on joint returns, as well as a surtax of .25% on incomes over $200,000 for singles and $250,000 for couples filing jointly. The city also levies a real estate transfer tax of 0.5% on the sale or exchange of real estate within the city limits.
Residents who leave New York City for more than 30 days will be subject to New York State taxes, which are levied at a higher rate than the city’s personal income tax – 12.8% for individuals and 25% for joint returns. The earned income tax rates in New York State are 4.41% and 8.82%, while the surtax rates are 0.9% and 1%. The real estate transfer tax is also higher in New York State – 2%.
Do I pay NYC tax if I live in NJ?
If you live in New York City and you earn income, you may be subject to New York City tax. However, if you live in Jersey and you earn income, you may be subject to New Jersey tax. In order to determine which tax system applies to you, it is important to understand your residency status.
If You Are a Resident of New York City:
You are a resident of New York City if your “home base” is in the city. Your home base is the place where you maintain your principal residence, or the place where you have a permanent habitation and intend to make it your principal residence. Whether or not you have a home base in the city depends on where your main activities take place. If you are an employee who works out of town part of the time, for example, your home base is probably outside of the city. But if you are a self-employed person whose office is within the city limits (and you use it as your principal residence), then your home base is likely within the city.
If You Are a Resident of Jersey:
You are a resident of Jersey if your primary residence is in Jersey or if you maintain a permanent habitation in Jersey and intend
Do I pay NYC tax if I live in Long Island?
If you reside in Nassau or Suffolk counties and own or rent property in New York City, you may be subject to New York City tax. In addition, if you are a US citizen living in New York City and your earnings are greater than $85,000, you may also be subject to US federal income tax.
There is no one answer to this question as the tax rates and collection procedures for NYC taxes can vary depending on your specific situation. However, some general tips that may help include:
Check with your accountant or the Tax Office to see if you are subject to any special NYC tax rates or collection procedures.
Make sure you keep all of your documentation related to your NYC tax payments (including copies of receipts from your tax preparation service) in case there are any questions or problems with the collection process.
Be prepared to pay any outstanding taxes plus interest and penalties. Time is of the essence when it comes to filing taxes and facing penalties for late payments.
If you have any questions about your NYC tax obligations, don’t hesitate to contact an accountant or the Tax Office.
How much is 100k after taxes in NYC?
If you’re a resident of New York City, you may be wondering how much money you’ll end up with after taxes are taken out. In this guide, we’ll outline the various tax rates and how they affect your income. We’ll also discuss how to collect taxes owed, including information on filing taxes and paying taxes. Let’s take a look!
new york city income tax rate 2022
Welcome to our New York City tax rates, collections guide! This article will provide you with all the information you need to know about the income tax rates in New York City for 2022.
The income tax rates in New York City for 2022 are as follows:
Individuals who earn $17,500 or less will have an income tax rate of 3.8%.
Individuals who earn between $17,500 and $92,500 will have an income tax rate of 5.4%.
Individuals who earn between $92,501 and $426,700 will have an income tax rate of 7.65%.
Individuals who earn between $426,701 and $1 million will have an income tax rate of 10.45%.
Individuals who earn more than $1 million will have an income tax rate of 12.85%.
new york city income tax rate history
The City of New York has an income tax rate schedule which applies to individuals, trusts, and estates. The 2018 taxes are based on taxable income from 2017. The 2019 tax rates were just announced and will be effective January 1, 2020.
The New York State Income Tax Law is complex and there are many provisions that can affect your individual situation. To help you understand your specific tax obligations, the New York City Department of Finance publishes an annual “Taxpayer’s Guide to New York City Taxation.” This guide provides a detailed analysis of each income tax bracket, as well as explanations of key terms used in the law.
If you’d like more detailed information about an individual income tax provision or would like to speak with one of our experienced tax preparers, please don’t hesitate to call us at 1-800-733-9291 or contact us online. We would be happy to assist you in preparing your 2018 NYC taxes.
new york city income tax rate 2021
Hello everyone!
It’s that time of year again – filing your taxes. But first, what do you need to know about the new york city income tax rate?
Income tax rates in New York City will change on January 1, 2021. Here’s a full guide on what you need to know about the new tax rates:
The highest income tax rate will decrease from 39.7% to 37% for single filers and from 43.4% to 41.1% for married couples filing jointly. The second highest income tax rate will decrease from 31.3% to 28%. The lowest income tax rate will decrease from 12% to 11%.
However, if your taxable income is above certain thresholds, you may still be required to pay the higher tax rate. For example, if your taxable income is $500,000 or more, you will still be taxed at the 39.7% rate.
In addition, there are other taxes that you may be responsible for paying in New York City. These taxes include real estate transfer taxes (7% of the sale price), business taxes (state and city), and luxury goods taxes (10%).
So
how to avoid new york city income tax
If you’re a New Yorker looking to avoid income tax, there are a few things you can do.
The first step is to figure out your adjusted gross income (AGI). This is your total taxable income minus any allowable deductions.
Next, figure out your tax bracket. This is the percentage of your AGI that will be taxed.
Finally, make sure you file your taxes using the correct form and with the correct information. New York City taxes are based on your Adjusted Gross Income, not your actual income. This means that you may have to take some special deductions to get below the threshold for taxation.
new york state tax on dividends
For residents of New York state, dividends received from stocks and other securities are subject to state income tax. The rate of state income tax on dividends is 4.5%, although the rate may change depending on your filing status and the type of dividend received.
In order to minimize state income taxes on dividend income, it is important to keep accurate records of all dividend payments and gross receipts from sales of stocks, bonds, and other securities. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with a tax advisor to determine the best way to structure your portfolio in order to minimize taxes.
If you have any questions about how dividends affect your New York state taxes, or if you need help preparing your tax return, please contact a licensed tax preparer.
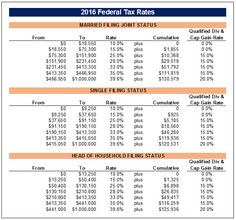
federal income tax rate
The highest federal income tax rate in the U.S. is 39.6%. The table below lists the individual income tax rates that apply to different filing statuses.
Single filers:
Taxable income: $0-$9,275
Tax: $0
10-29%
Taxable income: $9,276-$38,700
Tax: $3,812 (+10%)
30-39.6%
Taxable income: $38,701-$97,201
Tax: $8,526 (+30%)
40-49.4%
Taxable income: $97,202-$183,223
Tax: $17,424 (+40%)
Married couples filing jointly:
Taxable income: $0-$19,050
Tax: $0
Married couples filing separately:
Taxable income: $19,051 or more but less than $75,000
Taxes each spouse at his/her taxable income rate plus 0.5% of the spouse’s taxable income over $19,050