Learn About Being a Urologist
Urology is the medical specialty that provides diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases of the male and female urinary tract, kidneys, and bladder. The urologist treats diseases such as diabetes or kidney stones in men. Urologists also diagnose women who experience problems with their reproductive systems like infertility or cervical cancer.
Urologist requirements
To become a urologist, you’ll need to earn a medical degree, complete your residency program and apply for a license.
Urologist work environment
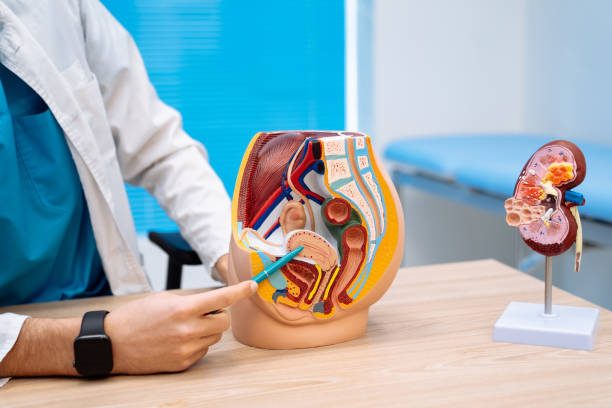
What does a urologist do
Urologists work in a variety of settings, including:
- Hospitals
- Doctor’s offices
- Ambulatory surgical centers
- Outpatient clinics (which may be located in hospitals or doctors’ offices)
- Research labs at universities and medical schools
- Schools for those studying to become urologists
Urologists can also practice in the following types of facilities:
- Government agencies such as the Public Health Service or Veterans Administration (VA)
- Private practices, which often employ several other physicians, nurses, technicians, and office staff
How to become a urologist?
What does a urologist do?
Once you’ve decided to become a urologist, you’ll need to complete the following steps.
- Medical school: Urologists must first earn an MD degree from an accredited medical school. This usually takes four years of full-time study, but can be completed in three years through other educational pathways.
- Medical internship: Following graduation from medical school, most aspiring urologists complete one year of internship training at a hospital or clinic under the supervision of experienced physicians. During this period they gain hands-on experience working with patients and learn various techniques used in treating diseases and injuries that affect the urinary tract system.
- Residency: After completing their internship year, prospective urologists move on to residency training—a three-year postgraduate program during which they learn how to treat patients using specific procedures within their specialty area. To become board certified by one’s professional organization (the American Board of Urology) after residency is completed, candidates must pass written examinations as well as clinical assessments demonstrating their knowledge and skill set in areas such as surgery and diagnostic imaging techniques like CT scans or MRIs (magnetic resonance imaging).
Urologist job description example
A urologist is a doctor who treats diseases of the urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. A urologist performs surgery to correct incontinence (inability to control urination) in men and women. They also perform surgery to correct male reproductive problems, such as sperm blockage caused by an injury or infection. Urologists treat cancerous growths in these organs as well as diseases of kidney stones.
Treat bladder cancer
What does a urologist do?
You may have heard of bladder cancer, and if you haven’t had a diagnosis yourself, you probably know someone who has. This is because it’s one of the most common cancers in men and women in the United States.
Bladder cancer is typically treated with surgery to remove all or part of the bladder (cystectomy), chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Sometimes patients need more than one treatment method at once, depending on how advanced their cancer is at diagnosis. Surgery can help prevent recurrence in some cases but doesn’t always work that way; it’s important to follow up closely with your urologist after treatment ends so they can monitor your progress and ensure that any side effects from treatment are managed properly.
Treat kidney cancer
In the United States, more than 70,000 people are diagnosed with kidney cancer each year. Kidney cancer is the most common type of kidney cancer and can be treated in a number of ways, including surgery and chemotherapy.
In this article, we’ll discuss the different types of treatment for kidneys affected by cancer as well as how to find a urologist who specializes in treating kidney tumors.
Treat prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men. It affects more than 1 in 7 men during their lifetime, and it is the second leading cause of cancer deaths among men. Because of this, it’s important to know what a urologist does and how they can help you if you have prostate cancer.
A urologist is an expert at treating prostate tumors and cancers, as well as other gynecological conditions affecting women and children. A urologist may also treat bladder problems such as incontinence or infections like interstitial cystitis (IC).
Treat kidney stones
Kidney stones are small, hard masses that form inside the kidneys. Typically, kidney stones do not cause any symptoms until they pass out of the body.
If you have a urinary tract infection (UTI), your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat it. In some cases, your doctor might recommend surgery on your bladder or urethra to remove the stone and repair any damage caused by it.
Repair male reproductive problems
A urologist is a doctor who treats urinary and reproductive health problems in men. Urologists specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of male reproductive problems, including erectile dysfunction and infertility. They also treat other sexual disorders that occur in men, such as premature ejaculation or impotence (male erectile dysfunction).
Perform surgery to correct incontinence
Sometimes, a patient will need surgery to correct incontinence. A urologist will perform a physical examination and then an ultrasound to determine the cause of the incontinence, which can often be traced back to prostate gland problems. After determining what is causing incontinence, the urologist will do a cystoscopy — where they insert their instrument through their patient’s urethra into the bladder — or an endoscopic retrograde ejaculation evaluation (ERAE). The ERAE involves taking samples from different parts of your prostate gland so that your urologist can find out whether this is affecting your ability to control urine flow. Finally, if necessary for diagnosis or treatment planning purposes, your doctor may want to perform additional procedures such as biopsies or injections into organs like your prostate gland or bladder muscles in order to test them for certain conditions.
Do cystoscopy and other tests
Cystoscopy is a procedure to look inside the bladder. It can be done on its own, but it’s often done in conjunction with other procedures like urodynamics and intravenous pyelograms (IVP).
A urologist specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases of the urinary tract.
A urologist specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases of the urinary tract. The urinary tract is a series of organs that functions to remove waste from the blood and to produce urine. The kidneys are responsible for filtering toxins from your blood, as well as for regulating your body’s water balance. When you urinate (pee), it comes from two small tubes called ureters that connect your kidneys to your bladder. If you have a UTI (urinary tract infection), it can be painful and lead to serious complications if left untreated. A doctor who specializes in treating these infections is called a urologist, who may also perform surgery on any part of this system including the bladder or prostate gland if need be
Conclusion
If you are interested in becoming a urologist, it is important to do your research on the job description and requirements. This will help you decide if this career path is right for you!