Business cycles are a part of economic life that have been around for centuries. They are the recurrent movements in GDP (Gross Domestic Product) over time, as well as fluctuations in employment, prices, and interest rates. In this article, we will be discussing what a business cycle is, its causes, and how it affects your business. So let’s get started!
What are types of business cycle?
There are three main types of business cycles: expansionary, contractionary and balanced. Here’s a brief description of each:
Expansionary Business Cycles
During an expansionary cycle, the economy is growing rapidly and businesses are expanding their operations. This can be due to increased demand from consumers or increased investment by businesses. This cycle is typically characterised by high levels of economic activity and optimism among the public.
Contractionary Business Cycles
During a contractionary cycle, the economy is shrinking rapidly and businesses are contracting their operations. This can be due to decreased demand from consumers or decreased investment by businesses. This cycle is typically characterised by low levels of economic activity and pessimism among the public.
Balanced Business Cycles
A balanced business cycle occurs when the economy experiences steady growth and neither expansion nor contraction. This type of cycle is usually considered to be the norm, but it can also occur during times of crisis (such as during a recession).
What is a business cycle example?
A business cycle is a recurring pattern of economic activity identified by the Federal Reserve. It is typically defined as a period of five years, but can be as short as one or two years or as long as ten or more years.
The most common type of business cycle is the recessions and depressions, which are periods of economic decline. Other types of cycles include booms and busts, which are periods of economic expansion and contraction, respectively; and expansions and contractions that vary in duration from a few months to many years.
What are the 4 phases of business cycle?
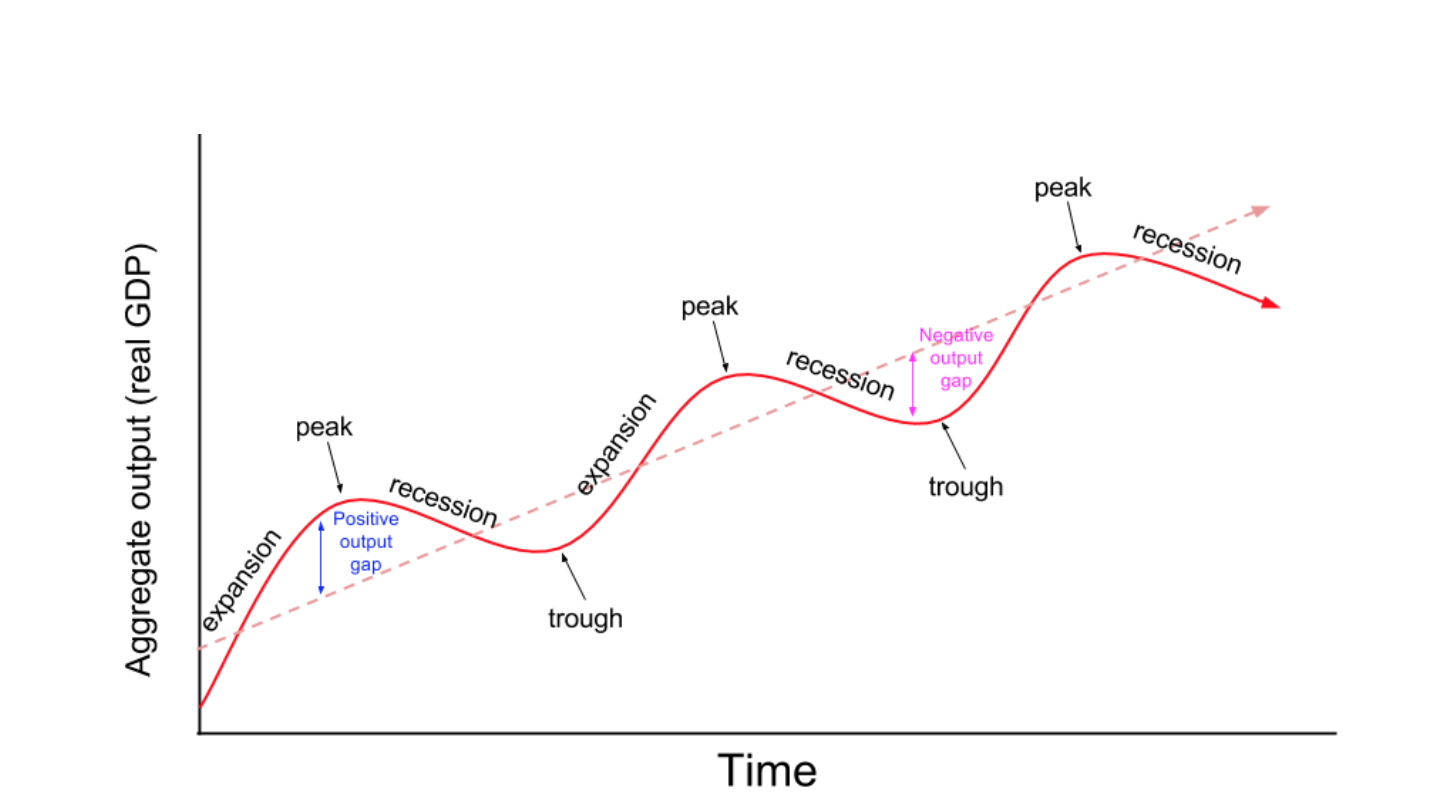
The business cycle is the name given to the cyclical changes that occur in the economy. It is made up of four phases: expansion, contraction, recession, and recovery.
Expansion: During the expansion phase, businesses are growing and hiring new employees. Fewer people are unemployed and more money is being spent than ever before. This is usually when prices are high and everyone is getting rich.
Contraction: The contraction phase marks a time when businesses are shrinking and layoffs are common. Prices start to decrease, and many people lose their jobs. At this stage, the economy may be in danger of entering into recession.
Recovery: The recovery phase begins when the economy has recovered from the recession. Companies start to hire again, and prices start to increase again. This is usually a happy time for most people, as they see their wealth grow
What are the 5 business cycles?
Business cycles are a time period that contain four phases: expansion, peak, contraction, and recession.
The following is a guide to understanding each of the business cycles:
1. Expansion phase: This is the stage in which businesses grow and create new jobs. Income increases and prices increase as well.
2. Peak phase: This is when businesses reach their maximum size and income. Prices and income reach their highest levels.
3. Contraction phase: This is the stage in which businesses reduce their workforce and income. Prices and income decrease as well.
4. Recession phase: This is the stage in which businesses close down and unemployment rises. Income decreases and prices decrease as well.
What is the importance of business cycle?
The business cycle is a time period of economic activity that typically lasts between one and four years. It’s often described as a “wave” of growth, expansion, and contraction.
There are two main types of business cycles: the secular (long-term) cycle and the cyclical (short-term) cycle.
The secular (long-term) business cycle is defined by general trends in economic activity that last for more than one year. The cyclical (short-term) business cycle is defined by fluctuations in economic activity that last for less than a year.
A key factor that influences the growth or decline of an economy is consumer spending. Consumers decide how much money to spend by buying items such as homes, cars, and electronics.
If consumers have more money, they will likely spend it on things such as cars, homes, and electronics. This will cause businesses to hire more employees, who will then spend their income on things like cars and homes. This will cause businesses to expand, which will create more jobs and increase consumer spending even further.
The main reason we have a secular (long-term) business cycle is because consumers have more money than they did
What is the purpose of the business cycle?
There are three primary purposes of the business cycle: to stimulate economic growth, to maintain price stability, and to distribute resources efficiently.
The United States has experienced a recession four times since World War II. What are the causes and consequences of a recession?
A recession is generally caused by a fall in demand for goods and services, which reduces employment and income. The consequences can be severe, including decreased consumer spending, falling stock prices and reduced residential and commercial real estate values.
What phase of business cycle is 2022?
The business cycle is a repeating pattern of economic growth and recession. There are four different phases of the business cycle: expansion, peak, contraction, and recovery.
Here is a full guide to each phase of the business cycle:
Expansion: This is the phase of the business cycle when businesses are expanding their operations and hiring new employees. The economy is growing rapidly and people are spending more money.
Peak: The peak phase of the business cycle is when businesses reach their maximum size and profitability. This is usually the most prosperous time for businesses.
Contraction: In the contraction phase, businesses are shutting down and laying off employees. The economy is contracting, and people are spending less money.
Recovery: The recovery phase begins when businesses start hiring new employees and expanding their operations again. The economy has returned to normal, and people are starting to spend more money.
What is business cycle and its stages?
A business cycle is a regular, predictable sequence of economic activity. There are three main types of business cycles: the normal cycle, the recessionary cycle, and the expansionary cycle.
The normal cycle is characterized by rising economic activity and unemployment rates that eventually fall back to their natural levels. This phase usually lasts about four years.
The recessionary cycle is marked by low economic activity and high unemployment rates. This phase usually lasts about two years.
The expansionary cycle is characterized by high economic activity and low unemployment rates. This phase usually lasts about six years.
What is the current business cycle?
The current business cycle is a time of expansions and contractions in the economy. The expansion phase usually lasts from late 2007 to early 2009, and the contraction phase usually lasts from late 2009 to early 2011.
What is another name of business cycle?
A business cycle is also known as an economic cycle, a financial cycle, or a recession.
How does business cycle affect the economy?
When the economy goes through a business cycle, it means that there are two different phases: expansion and contraction.
During the expansion phase, businesses are hiring more workers and making more products. This is because they believe that demand for their products will continue to grow.
However, when the cycle comes to an end, businesses start to cut back on their spending and layoffs occur. This is because they no longer believe that demand for their products will be as high as it was in the previous cycle.
What are the effects of business cycle?
Business cycles are a regular, predictable sequence of economic events that can be caused by changes in aggregate demand and aggregate supply. The four most common types of business cycles are the fiscal, paroxysmal, recessions, and expansions.
Fiscal cycle: The fiscal cycle refers to the cyclical variations in government spending and taxation. The fiscal cycle is largely determined by changes in tax rates and government spending programs. Tax rates are a function of income and inflationary pressures. Changes in government spending programs reflect current political priorities as well as changes in economic conditions.
Paroxysmal cycle: The paroxysmal cycle is characterized by episodes of rapid economic growth followed by periods of slower growth or recession. These episodes are typically associated with major changes in financial markets or the availability of credit.
Recessions: A recession is a period of depressed economic activity lasting two quarters or more. A recession is usually preceded by a decline in real GDP (Gross Domestic Product). A recession is followed by a period of recovery, during which real GDP rises above its previous level but remains below its pre-recession level.
Expansions: An expansion is a period of robust economic growth, marked by an increase in real
What are the characteristics of business cycle?
There are three main types of business cycles: the expansionary cycle, the contractionary cycle, and the mixed economy cycle.
The following are characteristics of each type of business cycle:
1. The expansionary cycle is typically characterized by an increase in investment, production, and employment. This is due to an increase in demand for goods and services.
2. The contractionary cycle is typically characterized by a decrease in investment, production, and employment. This is due to a decrease in demand for goods and services.
3. The mixed economy cycle is a combination of the two preceding cycles.
How long is a business cycle?
The business cycle is a time period where the economy goes through several consecutive phases. The length of a business cycle can vary, but it typically lasts around six months. There are three main stages to a typical business cycle: expansion, peak, and recession.
An expansion phase is when the economy is growing and businesses are hiring more employees. This is usually the most prosperous period for the economy as businesses are able to grow profits and hire new employees.
A peak phase is when the economy has reached its highest point and employment levels have stabilized. This is usually when businesses are making the most money and have the most customers.
A recession phase is when the economy begins to decline and employment levels decrease. This can cause a lot of businesses to go bankrupt and people to lose their jobs.
Who created the business cycle?
The business cycle is a term used to describe the years-long fluctuations in the economy. There are many different types of business cycles, but all share some common characteristics.
The first business cycle was created by Scottish economist Adam Smith in 1776. He described how markets go through repeated cycles of expansion and contraction. This theory is still used today to understand the economy.
Other types of business cycles include the boomerang, J-curve, and V-shape. Each has its own specific characteristics, but all involve a period of growth followed by a period of decline.
Knowing about the different types of business cycles can help you predict when the economy will start to decline or expand. It can also help you make more informed investment choices.