The goals of a central bank are typically to maintain price stability, promote economic growth, and support the currency. In some cases, a central bank may also aim to reduce inflation or financial instability. The goals of a central bank can change over time as the economy and monetary policy evolves.
To achieve its goals, a central bank must have clear objectives
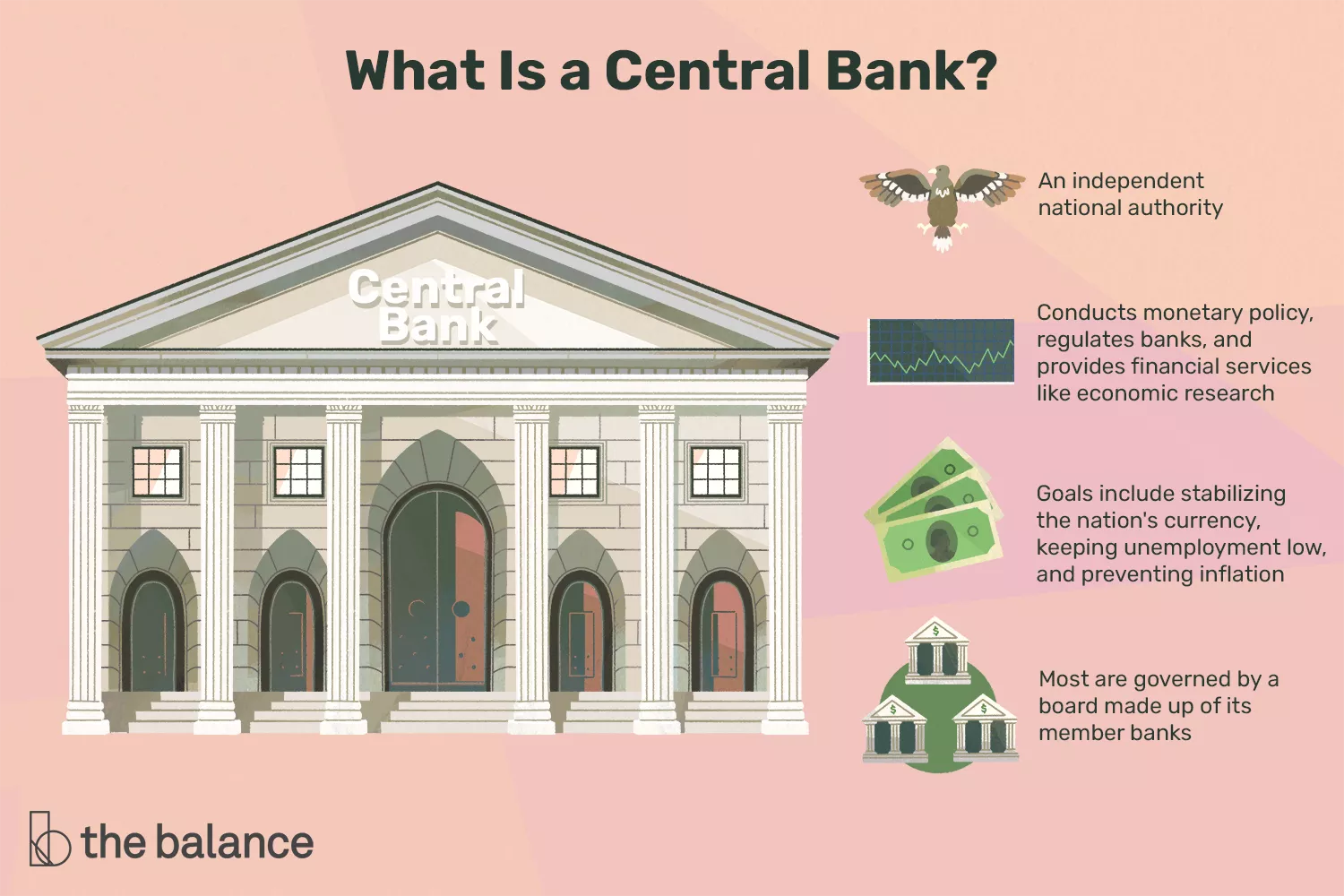
The primary goals of a central bank are to achieve stability in the financial system, foster economic growth, and promote price stability. Central banks also aim to keep inflation low and create jobs by driving down interest rates. In addition, they may also pursue other objectives, such as promoting international cooperation or managing foreign exchange reserves.
Central banks around the world have specific objectives that they strive to achieve in order to maintain stability and economic prosperity. The Federal Reserve Board of the United States, for example, is tasked with “maximizing long-term U.S. economic growth,” while the Bank of England is responsible for “promoting price stability and efficient financial markets.”
Primary goals of a central bank include (but are not limited to) price stability, full employment and financial system stability
A central bank’s primary goals include (but are not limited to) price stability, full employment and financial system stability. Other goals may include promoting economic growth, calming panics, and influencing interest rates. Many factors go into determining a central bank’s primary goal, including the economy’s state of health, the inflation rate, and the strength of the currency.
To achieve these objectives, the central bank may use a variety of tools and strategies
One tool that a central bank may use is interest rates. Interest rates influence the cost of borrowing money and can affect economic activity by influencing consumer spending, investment, and bank lending. Central banks may adjust interest rates in order to maintain macroeconomic stability or to promote certain economic goals.
Another tool that a central bank may use is regulation. Regulation can limit financial risks and help ensure that the banking system is functioning properly. Central banks may also engage in market interventions such as buying or selling government securities or issuing special loans to financial institutions.
Finally, a central bank may use liquidity injections or withdrawals to stabilize the economy. Liquidity injections provide money (liquidity) to businesses and individuals so that they can buy goods and services on credit. Withdrawals remove money from the economy so that people have less available to spend.
The five goals of a central bank are as follows: maximum employment, stable prices, moderate long-term interest rates, price stability and financial system stability
A central bank’s primary goals are as follows: maximum employment, stable prices, moderate long-term interest rates, price stability and financial system stability. These goals can be difficult to achieve simultaneously, and each goal has a different impact on the economy.
Maximum Employment: A central bank’s goal is to maintain full employment, which means that there is enough work for everyone who wants it. This is important because it ensures that people have income and resources to support themselves and their families. It also reduces the amount of pressure on the economy due to high levels of unemployment.
Stable Prices: A central bank tries to keep inflation under control by setting a target rate for the inflation rate. If the inflation rate rises above the target rate, the central bank will try to lower the target rate in order to bring it back below the inflation rate. Inflation can damage economies by causing wages to rise too fast or by making goods more expensive than they should be.
Moderate Long-Term Interest Rates: Central banks aim to keep long-term interest rates low so that banks can lend money easily and consumers can borrow money cheaply. This helps stimulate economic growth by making it easier for businesses to borrow money and for people to buy goods and services.
Price Stability: Another goal of a central bank is to maintain price stability, which means that prices for goods and services do not change over time (in terms of both quantity and quality). Price stability helps ensure that people have an
The 2 Types of Central Banks
A central bank’s primary goals can be divided into two categories: stabilization and inflation control.
Stabilization goals typically include preventing too much inflation or deflation, which could damage the economy and cause widespread financial instability. Central banks also aim to maintain price levels in an area that is consistent with the country’s economic development and sustainable over time.
Inflation control goals may involve setting a target rate of inflation, intervening in the money supply to prevent excessive growth in prices, or providing liquidity to support economic activity.
The Functions of a Central Bank
A central bank is an important institution in a capitalist economy, responsible for regulating the money supply and controlling interest rates. The primary goals of a central bank are to ensure price stability and economic growth.
A central bank’s ability to control the money supply is vital in maintaining stable prices. When demand for goods and services outstrips available supplies, prices rise. A central bank can use its power to buy up excess supplies of goods and drive down prices, preventing inflation from spiraling out of control.
Central banks also play an important role in promoting economic growth. When interest rates are too low, businesses have less incentive to invest in new projects. Low interest rates can also encourage people to take on more debt, which can lead to bubbles and financial crashes later on. By setting interest rates at a level that promotes healthy economic growth while preventing runaway inflation, a central bank helps preserve the stability of the financial system overall.
What determines a Central Bank’s Rate Policy
The objectives of a central bank’s rate policy can be broadly grouped into three categories: prosecuting price stability, maximizing employment, and providing monetary stimulus.
Accomplishing price stability has been the primary focus of central banks throughout history. A stable currency allows for economic growth while limiting inflationary pressures. Central banks that pursue a tight monetary policy to combat inflation may face political resistance from those who argue that higher prices are necessary for economic growth. Critics of too-tight monetary policies may argue that they cause strains in financial markets and lead to prolonged periods of high unemployment.
Central banks are tasked with maintaining the overall health of the economy
A central bank is a financial institution that manages the country’s money supply and sets interest rates. Its primary goals are to maintain the overall health of the economy by ensuring that inflation is under control and that banks have enough liquidity to meet their lending needs.
The Fed’s primary goal is to keep inflation low and stable. It does this by setting interest rates and providing liquidity to banks. The Bank of Japan tries to achieve similar goals by buying government bonds and other securities, which pushes down the yen and encourages investment in Japan.
Some central banks also focus on macroeconomic stability, such as preventing large swings in economic output or prices. Others focus on specific areas, such as housing or employment.
Their objectives can be summarized as follows:
The following are some common objectives that central banks may have:
A. To maintain price stability
A central bank’s goals are to maintain price stability and promote economic growth. Price stability is defined as a general tendency for prices to remain within certain bounds, while promoting economic growth is the goal of increasing the amount of goods and services available in the market for people to purchase.
In order to achieve these goals, a central bank typically uses different techniques, including setting interest rates, buying and selling securities, and providing liquidity to the banking system. Additionally, a central bank may use reserve requirements or quantitative easing (QE) to influence the amount of money available in circulation.
B. To foster economic growth
A central bank’s primary goal is to foster economic growth. This can be done by influencing interest rates, providing liquidity to the banking system, and providing supportive monetary policies.
1) Influence interest rates. A central bank can influence interest rates by purchasing or selling government bonds or other securities. By doing so, the central bank affects short-term interest rates and makes it more difficult for people and businesses to borrow money. This can help to stimulate the economy by making borrowing cheaper and encouraging people and businesses to invest in new projects.
2) Provide liquidity to the banking system. A central bank can provide liquidity to the banking system by buying or selling government securities or cash. By doing so, the central bank creates money that can be used to buy goods and services from businesses. This helps to ease financial pressure on businesses and keeps prices stable.
3) Provide supportive monetary policies. A central bank can provide supportive monetary policies by printing new currency or lending money directly to banks. Doing so helps keep banks flush with cash and encourages them to lend money to businesses and consumers.
C. To promote financial stability
The primary goals of a central bank are to promote financial stability, maintain price stability, and support the economy. In order to achieve these goals, a central bank typically implements a variety of policies and strategies.
One of the most common policies is interest rate regulation. This involves setting a target interest rate for commercial banks and other lending institutions, and using monetary policy to adjust the rate when it falls below or rises above the target. Another policy is reserve requirements. This requires banks to hold a certain percentage of their deposits in reserves, which helps prevent them from speculating with those funds. Central banks also use other tools, such as liquidity facilities and credit ratings, to try to influence financial markets.
While each central bank has unique policies and goals, all aim toward promoting financial stability and helping the economy grow.
D. To achieve maximum employment
A central bank’s primary goals are to achieve maximum employment and price stability. Other objectives, such as promoting economic development or financial stability, may be secondary goals. A central bank’s approach to achieving these goals will vary depending on the country and the economy. In general, a central bank will use a variety of measures to stimulate the economy, including lowering interest rates or injecting money into the system.
E. To protect the currency
A central bank’s primary goals are to protect the currency and maintain economic stability. A central bank is responsible for issuing currency, overseeing the banking system, and providing financial services. Central banks also play a role in macroeconomic management.
F. To support foreign exchange reserves and foreign investment
A central bank’s primary goals include maintaining stability in the economy, fostering economic growth, and supporting foreign exchange reserves and foreign investment. In addition, a central bank may also aim to protect consumer interests and promote financial sector stability. A central bank’s objectives can change over time as the economy changes.
conclusion
A central bank is an institution that manages the nation’s money and provides financial stability. Its primary goals are to promote economic growth, maintain price stability, and provide financial services to the public.
A central bank’s goals may change over time, depending on the economic conditions of the country. Typically, a central bank will focus on developing policies that will help achieve its primary goals. This can include providing credit to businesses and individuals, implementing interest rates and buying or selling government securities.